|

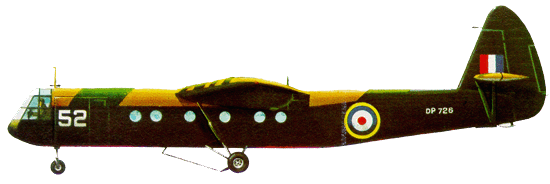
The Airspeed AS.51
Horsa was a World War II troop-carrying glider built by the British
company Airspeed Ltd and subcontractors. It was named after the 5th
century warrior Horsa and was used for air assault by British and
Allied armed forces.
The use of assault
gliders by the British was prompted by the use by Germany of the DFS
230, which was first used in May 1940
to successfully assault the Eben Emael fort in Belgium. Their advantage
compared to parachute assault was that the troops were landed together
in one place, rather than being dispersed.
With around 28 troop
seats, the Horsa was much bigger than the 13-troop American Waco CG-4A
(known as the Hadrian by the British), and the 8-troop
General Aircraft Hotspur glider which
was intended for training duties only. As well as troops, the AS51
could carry a jeep or a 6 pounder gun. The AS.58 Horsa Mk.II had
a hinged nose section, reinforced floor and double nose wheels to
support the extra weight of vehicles.
The Horsa was first
used in combat on July 10, 1943, when 27 were used in the invasion of
Sicily. Large numbers were subsequently used in the Normandy, Operation
Dragoon, Operation Market Garden, and Operation Varsity (Crossing the
river Rhine). In Normandy, the first troops to land in France did so
using Horsas, capturing Pegasus Bridge.

On operations they were
towed variously by Stirling, Halifax, Albemarle, Whitley and C-47
Dakota tugs, using a harness that attached to both wings. Glider pilots
were usually from the Glider Pilot Regiment, part of the Army Air
Corps, although Royal Air Force pilots were used on occasion. The Horsa
was also used in service by the USAF.
On June 5, 2004, as part of the 60th anniversary commemoration of
D-Day, Prince Charles unveiled a replica Horsa on the site of the first
landing at Pegasus Bridge, and talked with the original pilot of the
aircraft, Jim Wallwork.
Design and manufacture
The Horsa was designed to specification X.26/40 and built from 1940
onwards. It first flew on 12 September, 1941. The Horsa featured a
high-wing and was of all-wooden construction due to the shortage of
other materials and the expendable nature of the aircraft. It was one
of the first gliders equipped with a tricycle undercarriage for
take-off. On operational flights this was jettisoned and landing was
made on a skid under the fuselage. The wing carried large, 'barn door'
flaps, which when lowered conferred a steep high rate-of-descent
landing that allowed the pilots to land in constricted areas.
The Horsa was considered sturdy and very manoeuvrable for a glider.
3655 were built by Airspeed as well as companies outside the aircraft
industry such as Austin Motors and the furniture manufacturers Harris
Lebus. The gliders were built in a number of sections, each produced in
a separate factories in case of German attack.
Specifications
Type: Assault Glider
Origin: Airspeed
Models: Horsa I and II
First Flight: Prototype DG597: September 12, 1941
Service Delivery: DP279: May 1942
Number Produced: 3,644
General characteristics
Crew: 2
Capacity: 25 passengers
Length: 67 ft (20.4 m)
Wingspan: 88 ft (26.8 m)
Height: 21 ft (6.4 m)
Wing area: 1,148 ft² (106.7 m²)
Empty: 7,500 lb (3,400 kg)
Loaded: 15,250 lb (6,920 kg)
Maximum takeoff: lb ( kg)
Performance
Towing speed: 127 mph (204 km/h)
Gliding speed: 100 mph (160 km/h) |
